Women in the United States continue to earn less than men, on average. Among full-time, year-round workers in 2019, women’s median annual earnings were 82% those of men.
The gender wage gap is narrower among younger workers nationally, and the gap varies across geographical areas. In fact, in 22 of 250 U.S. metropolitan areas, women under the age of 30 earn the same amount as or more than their male counterparts, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of Census Bureau data.


The New York, Washington, D.C., and Los Angeles metropolitan areas are among the cities where young women are earning the most relative to young men. In both the New York and Washington metro areas, young women earn 102% of what young men earn when examining median annual earnings among full-time, year-round workers. In the Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim metro area, the median earnings for women and men in this age group were identical in 2019.
Overall, about 16% of all young women who are working full time, year-round live in the 22 metros where women are at or above wage parity with men.
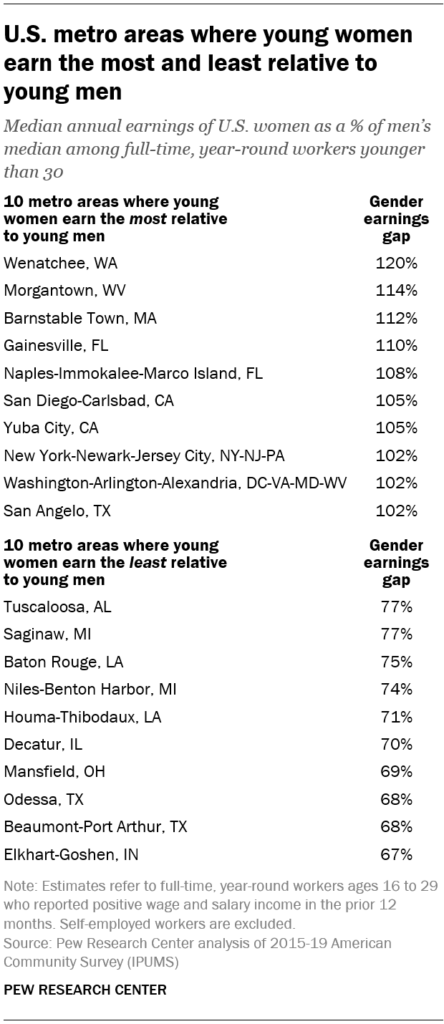

There are 107 metros where young women earn between 90% and 99% of what young men earn. Nearly half (47%) of young women working full time, year-round lived in these areas in 2019.
In another 103 metros, young women earn between 80% and 89% of what men earn. These areas were home to 17% of young women who were employed full time, year-round in 2019.
And in 14 metros, young women’s earnings were between 70% and 79% those of men in 2019. About 1% of the young women’s workforce lived in these metros.
In four metro areas – Mansfield, Ohio; Odessa, Texas; Beaumont-Port Arthur, Texas; and Elkhart-Goshen, Indiana – women younger than 30 earn between 67% and 69% of what their male counterparts make. These metros account for 0.3% of the young women’s workforce. (Some 19% of young women in the workforce are employed in metros where earnings data is not available or are in nonmetropolitan areas.)
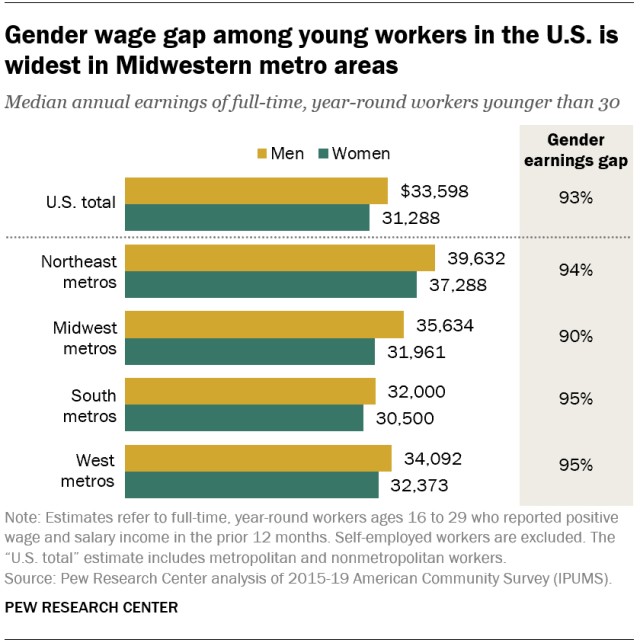

From a regional perspective, metropolitan areas in the Midwest tend to have wider gender wage gaps among young workers. Young women working full time, year-round in Midwestern metros earn about 90% of their male counterparts. In other regions, by comparison, young women earn 94% or more of what young men earn.
Nationally, women under 30 who work full time, year-round earn about 93 cents on the dollar compared with men in the same age range, measured at the median. As these women age, history suggests that they may not maintain this level of parity with their male counterparts. For example, in 2000, the typical woman age 16 to 29 working full time, year-round earned 88% of a similar young man. By 2019, when people in this group were between the ages of 35 and 48, women were earning only 80% of their male peers, on average. Earnings parity tends to be greatest in the first years after entering the labor market.
Labor economists examine earnings disparities among full-time, year-round workers in order to control for differences in part-time employment between men and women as well as attachment to the labor market. However, even among full-time, year-round workers, men and women devote different amounts of time to work. Men under 30 usually work 44 hours per week, on average, compared with 42 hours among young women.
(Courtesy PEW. By Richard Fry, senior researcher focusing on economics and education at Pew Research Center)